Definitive Guide to Sourcing Optifoam Dressing for Superior
Guide to Optifoam Dressing
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for optifoam dressing
- Understanding optifoam dressing Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of optifoam dressing
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for optifoam dressing
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for optifoam dressing
- Manufacturing Processes for Optifoam Dressing
- Quality Assurance and Control (QA/QC) Framework
- Verifying Supplier Quality Controls: Actionable Strategies for B2B Buyers
- Navigating QC and Certification Nuances for Global Markets
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for optifoam dressing Sourcing
- Spotlight on Potential optifoam dressing Manufacturers and Suppliers
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for optifoam dressing
- Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the optifoam dressing Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of optifoam dressing
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for optifoam dressing
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for optifoam dressing
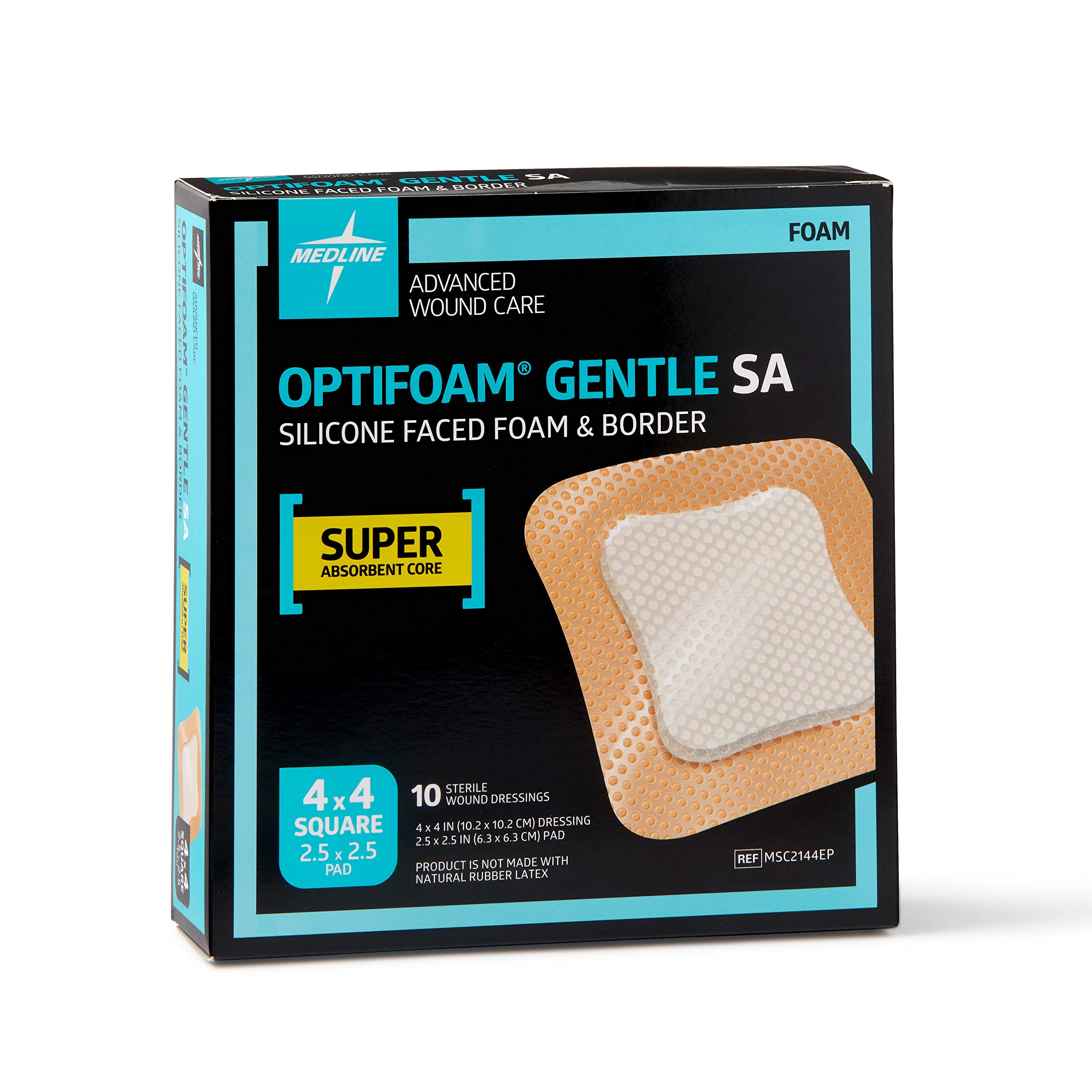
Optifoam dressings represent a pivotal advancement in modern wound care, combining superior moisture management and gentle adhesion to promote optimal healing environments. For international B2B buyers—especially those operating in diverse and growing healthcare markets such as Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, Brazil, and various European countries—understanding the nuances of optifoam products is essential to meet clinical demands and regulatory standards effectively. These dressings are widely used to prevent pressure injuries and treat a range of wounds, including ulcers, burns, and skin tears, making them indispensable in both acute and chronic care settings.
This comprehensive guide delves into the critical aspects of optifoam dressings, providing a detailed exploration of product types, materials technology, manufacturing processes, and quality control measures. Buyers will gain insight into the global supplier landscape, enabling them to identify reliable partners who meet stringent international quality benchmarks. Cost considerations and market trends are also examined, helping procurement professionals to balance budget constraints with clinical efficacy.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
By addressing frequently asked questions and highlighting region-specific sourcing challenges, this resource empowers buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to make informed, strategic purchasing decisions. Whether sourcing for hospitals, clinics, or home health providers, understanding the full spectrum of optifoam dressing options ensures improved patient outcomes and operational efficiency in wound management.
Understanding optifoam dressing Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Optifoam Gentle | Silicone adhesive border, highly conformable, breathable | Sensitive skin, fragile wounds, frequent dressing changes | Pros: Gentle adhesion reduces trauma; Cons: Higher cost vs. basic foam |
| Optifoam Basic | Non-adhesive, absorbent foam, simple design | General wound care, moderate exudate wounds | Pros: Cost-effective, versatile; Cons: Requires secondary fixation |
| Optifoam Adhesive | Foam with adhesive border, moderate conformability | Pressure ulcers, post-op wounds, moderate to heavy exudate | Pros: Secure fit, reduced leakage; Cons: May cause mild skin irritation |
| Optifoam Sacrum | Large size, contoured for sacral area, adhesive border | Pressure injury prevention and treatment on sacrum | Pros: Specialized shape for sacrum; Cons: Limited to specific wound sites |
| Optifoam Bordered | Multi-layer bordered foam with waterproof outer layer | High-risk pressure injuries, surgical wounds | Pros: Enhanced protection, fluid management; Cons: Bulkier, higher price |
Optifoam Gentle
This variant features a silicone adhesive border designed for gentle adherence and easy repositioning, making it ideal for patients with sensitive or fragile skin. It allows moisture vapor transmission to optimize the wound environment and can remain in place up to seven days depending on drainage. For B2B buyers in regions with limited skilled wound care providers, its ease of use and reduced trauma during dressing changes can improve patient outcomes and reduce training needs, though it typically carries a premium price.
Optifoam Basic
Optifoam Basic is a non-adhesive foam dressing that offers excellent absorbency and cushioning for a wide range of wound types. It requires a secondary fixation method such as bandages or tapes, which can be advantageous in settings where adhesive sensitivity is a concern. This version is cost-effective and versatile, making it attractive for bulk procurement by healthcare facilities in emerging markets seeking budget-friendly yet reliable wound care options.
Optifoam Adhesive
Combining foam absorbency with an adhesive border, Optifoam Adhesive provides a secure fit suitable for moderate to heavily exuding wounds such as pressure ulcers or post-operative sites. Its moderate conformability helps reduce leakage and contamination risks. Buyers should consider its balance between adhesion strength and skin tolerance, especially in climates prone to perspiration. This dressing is suitable for hospitals and clinics requiring dependable, long-lasting wound coverage.
Optifoam Sacrum
Specifically designed for sacral wounds, this dressing features a larger, anatomically contoured shape with an adhesive border to maintain placement on difficult-to-dress areas prone to pressure injuries. It supports prevention and treatment strategies in high-risk patients, a key consideration for institutions managing long-term care or surgical recovery. Procurement should factor in wound site specificity and inventory management to optimize usage.
Optifoam Bordered
This multi-layer bordered foam dressing includes a waterproof outer layer and enhanced fluid management capabilities, making it ideal for high-risk pressure injuries and surgical wounds requiring robust protection. While it offers superior wound environment control, its increased bulk and higher cost may impact purchasing decisions in budget-sensitive markets. Strategic deployment in critical care settings can maximize clinical benefits and justify investment.
Related Video: Large Language Models (LLMs) – Everything You NEED To Know
Key Industrial Applications of optifoam dressing
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of optifoam dressing | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare & Hospitals | Management of chronic wounds and pressure ulcers | Reduces patient recovery time and lowers risk of infection | Compliance with international medical standards, availability of sterile packaging, shelf life |
| Elderly Care Facilities | Prevention and treatment of skin tears and pressure injuries | Enhances patient comfort and reduces incidence of complications | Ease of application/removal, hypoallergenic properties, cost-effectiveness for bulk purchasing |
| Sports Medicine & Rehabilitation | Treatment of acute injuries such as abrasions and lacerations | Facilitates faster healing, minimizes dressing changes | Flexibility and conformability of dressing, moisture management, durability under movement |
| Military & Emergency Services | Wound care in field conditions for trauma and burns | Provides reliable protection and pain relief in austere settings | Robust packaging, ease of transport, multi-day wear capability, compatibility with other first aid supplies |
| Home Healthcare Providers | Post-surgical wound care and management of leg ulcers | Enables effective outpatient care, reducing hospital readmissions | Availability in various sizes, ease of use by non-professionals, clear instructions in multiple languages |
Healthcare & Hospitals
In hospital settings across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, optifoam dressings are critical for managing chronic wounds, pressure ulcers, and surgical sites. These dressings create an optimal moist environment to accelerate healing and reduce infection risk. Hospitals benefit from decreased patient stays and improved clinical outcomes. Buyers should prioritize sourcing dressings compliant with international health regulations (e.g., CE marking, FDA approvals) and ensure sterile packaging suitable for diverse climates and storage conditions.
Elderly Care Facilities
Elderly care centers often deal with fragile skin prone to tears and pressure injuries. Optifoam dressings provide gentle adhesion and cushioning, minimizing trauma during dressing changes. This reduces patient discomfort and lowers treatment costs by preventing wound worsening. For B2B buyers in regions like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia, selecting hypoallergenic options with easy application is essential. Bulk procurement with cost efficiency and reliable supply chains ensures continuous care quality.
Sports Medicine & Rehabilitation
Sports clinics and rehabilitation centers use optifoam dressings for acute injuries such as abrasions, lacerations, and partial-thickness wounds. The dressings’ conformability and moisture vapor transmission support dynamic movement while maintaining wound protection. This allows athletes to recover faster with fewer dressing changes. Buyers should assess product flexibility, breathability, and durability, especially for markets with high activity levels and warm climates.
Military & Emergency Services
In military and emergency response operations, optifoam dressings serve as essential first-line wound care for trauma, burns, and skin injuries in challenging environments. Their multi-day wear capability and pain-reducing silicone borders are vital for field use where frequent dressing changes are impractical. Procurement in Middle Eastern and African defense sectors must focus on robust packaging for transport, extended shelf life, and compatibility with other emergency medical supplies.
Home Healthcare Providers
With the rise of outpatient and home-based care globally, optifoam dressings are increasingly used for post-surgical wounds and chronic leg ulcers. Their ease of use and gentle removal make them suitable for patients and caregivers without medical training. International buyers should consider dressings available in multiple sizes and with multilingual instructions to accommodate diverse populations. Reliable supply chains and local regulatory compliance are also key for effective home healthcare distribution.
Related Video: How to Apply Medline Optifoam Gentle Silicone Face and Border Dressing?
Strategic Material Selection Guide for optifoam dressing
Analysis of Common Materials for Optifoam Dressing
Optifoam dressings primarily utilize advanced foam materials combined with adhesive borders and protective layers to optimize wound healing. Selecting the right material for these dressings is critical for manufacturers and international B2B buyers, especially in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where environmental conditions, regulatory standards, and healthcare infrastructure vary widely.
1. Polyurethane Foam
Key Properties:
Polyurethane foam is highly absorbent, flexible, and breathable, with excellent moisture vapor transmission rates (MVTR). It maintains structural integrity under pressure and adapts well to body contours, making it suitable for pressure ulcer prevention and management. It is chemically stable across a broad temperature range (typically -40°C to 80°C).
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Excellent fluid management, cushioning effect, lightweight, and cost-effective. It supports a moist wound environment conducive to healing.
– Cons: Can degrade with prolonged exposure to UV light and may not be suitable for highly exudative wounds without additional layers. Manufacturing complexity is moderate due to the need for precise pore size control.
Impact on Application:
Polyurethane foam is compatible with a wide range of wound types, including partial and full-thickness wounds, burns, and abrasions. It performs well in humid climates common in Africa and the Middle East but may require additional packaging protection for export to regions with intense sunlight exposure.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, and Europe should verify compliance with ASTM standards for biocompatibility and MVTR. European markets may require CE marking and adherence to ISO 10993 for medical devices. Cost sensitivity in South America and Africa may favor polyurethane foam dressings due to their balance of performance and affordability.
2. Silicone Adhesive Border
Key Properties:
Silicone adhesives provide gentle but secure adhesion, minimizing trauma during dressing changes. They maintain adhesion in moist and oily skin environments and allow for repositioning without losing stickiness.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Reduces pain and skin damage, hypoallergenic, and suitable for fragile skin types. Enhances patient comfort and compliance.
– Cons: Higher material cost and manufacturing complexity compared to traditional adhesives. May have limited shelf life under extreme temperature fluctuations.
Impact on Application:
Ideal for sensitive skin and chronic wound patients, silicone borders ensure dressing stability without compromising skin integrity. This is particularly important in regions with high temperatures and sweating, such as the Middle East and parts of Africa.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Regulatory approval for medical-grade silicone adhesives is essential, with FDA or CE certification preferred. Buyers should consider local climate conditions impacting adhesive performance and storage. In Europe, compliance with MDR (Medical Device Regulation) is mandatory.
3. Hydrophilic Foam Layers
Key Properties:
Hydrophilic foams attract and retain wound exudate, maintaining a moist healing environment. They balance absorption with moisture vapor permeability, preventing maceration.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Enhances wound healing by managing exudate effectively, reduces dressing change frequency, and improves patient outcomes.
– Cons: Typically more expensive than standard polyurethane foams and may require more complex manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application:
Especially suitable for wounds with moderate to heavy exudate, common in diabetic ulcers and venous leg ulcers. Hydrophilic foam dressings are beneficial in humid climates where moisture management is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should assess product certifications for biocompatibility and fluid handling capacity. In markets like South America and Africa, cost versus benefit analysis is crucial, as higher-priced hydrophilic foams may be justified by reduced dressing changes and improved healing times.
4. Polyethylene Film Backing
Key Properties:
Polyethylene film is a semi-permeable backing layer that provides a waterproof barrier while allowing moisture vapor to escape. It protects the wound from external contaminants and mechanical stress.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Durable, cost-effective, and provides excellent protection against bacteria and fluids. Easy to manufacture and integrate with foam layers.
– Cons: Limited breathability compared to more advanced films, potential for skin irritation if adhesive compatibility is poor.
Impact on Application:
Polyethylene film backing is widely used in optifoam dressings to ensure durability and protection, especially in environments with high infection risk. It is suitable for use in hospital and home care settings across diverse climates.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with international standards like ASTM F1671 for viral penetration resistance is important. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should verify that the film meets local environmental regulations regarding plastic use and disposal.
Summary Table of Materials for Optifoam Dressing
| Material | Typical Use Case for optifoam dressing | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyurethane Foam | Absorbent core for pressure ulcers, burns, abrasions | High absorbency and flexibility | UV sensitivity, moderate manufacturing complexity | Low |
| Silicone Adhesive Border | Adhesive border for gentle, secure attachment | Minimizes skin trauma, repositionable | Higher cost, sensitive to temperature extremes | High |
| Hydrophilic Foam Layers | Managing moderate to heavy exudate wounds | Superior moisture management and healing support | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Polyethylene Film Backing | Protective outer layer against fluids and contaminants | Durable, waterproof, cost-effective | Less breathable, potential skin irritation | Low |
This guide assists international B2B buyers in selecting optifoam dressing materials tailored to their regional requirements, regulatory environments, and budget constraints, ensuring optimal wound care product performance and market success.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for optifoam dressing
Manufacturing Processes for Optifoam Dressing
The production of optifoam dressings involves a carefully controlled sequence of stages designed to ensure optimal wound care performance. Understanding these steps can help international B2B buyers evaluate supplier capabilities and product quality effectively.
1. Material Preparation
- Raw Material Selection: The process begins with sourcing high-quality polyurethane foam substrates, medical-grade silicone adhesives, and breathable backing films. Suppliers typically use hydrophilic foam to ensure effective absorption and moisture management.
- Pre-treatment: Foam materials undergo conditioning processes such as cutting into precise sheets, sterilization, and surface treatments to enhance adhesion properties and biocompatibility.
2. Forming and Shaping
- Cutting and Molding: Automated die-cutting machines shape the foam into specific dressing sizes and profiles, including contours for anatomical fit (e.g., sacrum or limb-specific shapes).
- Layer Integration: Multiple foam layers may be laminated together to create multi-layered dressings with enhanced absorption and cushioning properties.
- Edge Finishing: Edges are trimmed and sealed to prevent fraying and ensure patient comfort.
3. Assembly
- Adhesive Application: Medical-grade silicone adhesives are uniformly applied as a border around the foam pad to provide gentle yet secure adhesion to the skin, allowing for repositioning without trauma.
- Backing Layer Attachment: A moisture vapor permeable backing film is laminated to the foam to protect the wound from external contaminants while allowing breathability.
- Border Reinforcement: Borders may be reinforced with low-friction outer layers to reduce shear and friction during patient movement.
4. Finishing and Packaging
- Sterilization: Finished dressings undergo sterilization processes such as gamma irradiation or ethylene oxide treatment to meet aseptic standards.
- Quality Inspection: Dressings are inspected for dimensional accuracy, adhesive uniformity, and packaging integrity.
- Packaging: Individual sterile dressings are sealed in medical-grade pouches with clear labeling for size, lot number, and expiration date, facilitating traceability.
Quality Assurance and Control (QA/QC) Framework
Robust quality management is critical for wound care products like optifoam dressings, as they directly impact patient outcomes. International B2B buyers should seek suppliers with comprehensive QA/QC systems aligned with global standards.
Relevant International Standards and Certifications
- ISO 9001: Specifies requirements for a quality management system (QMS) ensuring consistent product quality and continuous improvement.
- ISO 13485: The medical device QMS standard, critical for manufacturers of wound care dressings, focusing on risk management and regulatory compliance.
- CE Marking (Europe): Demonstrates conformity with EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR) requirements for safety and performance.
- FDA 510(k) Clearance (USA): Indicates compliance with U.S. regulatory standards for medical devices.
- Other Regional Certifications: For markets in Africa, South America, and the Middle East, certifications from local regulatory bodies (e.g., Saudi FDA, ANVISA Brazil, NAFDAC Nigeria) may be required or preferred.
Key Quality Control Checkpoints
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection and testing of raw materials such as foam density, adhesive tackiness, and film permeability before manufacturing.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during production stages including dimensional checks, adhesive application uniformity, and lamination integrity.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive inspection of finished dressings for sterility, packaging seal integrity, physical defects, and labeling accuracy.
Common Testing Methods
- Absorption and Retention Testing: Evaluates the dressing’s capacity to absorb and retain wound exudate under simulated conditions.
- Moisture Vapor Transmission Rate (MVTR): Measures breathability to ensure an optimal moist healing environment.
- Adhesion Strength Testing: Assesses silicone border adhesion to skin analogs, balancing secure attachment with gentle removal.
- Biocompatibility Testing: Includes cytotoxicity, sensitization, and irritation studies to confirm skin safety.
- Sterility Assurance: Validates sterilization effectiveness through biological indicators and endotoxin testing.
Verifying Supplier Quality Controls: Actionable Strategies for B2B Buyers
For international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, ensuring supplier quality extends beyond certifications. Practical verification steps include:
- Factory Audits: Conduct on-site or virtual audits focusing on QMS implementation, manufacturing environment controls, and employee training. Audits can be performed by the buyer or trusted third-party inspection agencies.
- Review of Quality Documentation: Request and evaluate batch production records, material certificates of analysis (CoA), sterilization validation reports, and stability data.
- Third-Party Testing: Engage independent laboratories to perform sample testing, verifying compliance with claimed product specifications.
- Supplier Qualification Programs: Establish long-term partnerships based on consistent quality performance, periodic re-assessments, and corrective action follow-ups.
- Regulatory Compliance Checks: Confirm that the supplier’s certifications are current and recognized in your target markets, noting that some regions may require additional local approvals.
Navigating QC and Certification Nuances for Global Markets
International buyers should be aware of specific considerations depending on their region:
- Africa (e.g., Nigeria): NAFDAC registration is often mandatory. Buyers should ensure that imported dressings comply with both international standards and local regulations, including labeling in English or local languages where required.
- South America: Regulatory agencies like ANVISA in Brazil require detailed product dossiers and may conduct local inspections. Certificates such as CE or FDA clearance facilitate approvals but do not replace local registration.
- Middle East (e.g., Saudi Arabia): The Saudi Food and Drug Authority (SFDA) enforces strict device registration and post-market surveillance. Suppliers must provide technical files and may need local agent representation.
- Europe: Compliance with MDR and CE marking is essential, with increased scrutiny on clinical evaluation and post-market clinical follow-up (PMCF). Buyers should verify the Notified Body involved and ensure traceability via Unique Device Identification (UDI).
By understanding these manufacturing and quality assurance intricacies, B2B buyers can make informed procurement decisions, ensuring optifoam dressings meet stringent safety, efficacy, and regulatory demands across diverse international markets.
Related Video: Our manufacturing process: Textiles
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for optifoam dressing Sourcing
Understanding the cost and pricing dynamics of Optifoam dressings is essential for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize procurement strategies and achieve cost-effective wound care solutions. This analysis breaks down key cost components, pricing influencers, and practical buyer tips tailored for markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Key Cost Components in Optifoam Dressing Production
-
Materials
The primary cost driver is the high-quality foam substrate combined with advanced silicone adhesive borders, which provide conformability and gentle adhesion. Specialty materials that regulate moisture vapor transmission rates (MVTR) add to raw material expenses. Sourcing medical-grade, hypoallergenic components compliant with international health standards typically increases material costs. -
Labor and Manufacturing Overhead
Skilled labor is required for precision manufacturing, particularly in applying silicone borders and ensuring uniform foam density. Overhead includes factory utilities, equipment maintenance, and compliance with stringent quality assurance processes mandated for medical devices. -
Tooling and Equipment
Initial setup costs for tooling to produce specific dressing sizes and configurations are significant. Custom molds or dies may be necessary for specialized product lines like sacral or gentle variants, impacting upfront capital expenditure. -
Quality Control (QC)
QC includes rigorous testing for biocompatibility, absorption capacity, and sterility, which is crucial for medical dressings. This step ensures compliance with regulatory certifications (e.g., CE marking, FDA approval), adding to per-unit costs. -
Logistics and Distribution
Due to the sensitive nature of wound care products, logistics involve temperature-controlled storage and handling, especially for international shipments. Freight costs, customs duties, and import taxes vary by region and affect landed cost. -
Profit Margin
Manufacturers and distributors factor in margins to cover R&D, marketing, and after-sales support. Margins can fluctuate based on market demand and competitive positioning.
Influencing Factors on Pricing
-
Order Volume and Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ)
Bulk purchasing typically secures lower unit prices. However, MOQs can be challenging for smaller healthcare providers or distributors in emerging markets. -
Product Specifications and Customization
Variants like Optifoam Gentle or Sacral dressings may command premium pricing due to specialized features. Custom sizing or packaging tailored to local preferences also influences cost. -
Material Quality and Certifications
Dressings with internationally recognized certifications (ISO, CE, FDA) often carry higher prices but assure quality and safety, critical in healthcare procurement. -
Supplier Reliability and Location
Established suppliers with robust supply chains and after-sales support justify premium pricing. Geographic proximity can reduce logistics costs and delivery times. -
Incoterms and Shipping Terms
Price negotiations must consider terms like FOB, CIF, or DDP, which allocate responsibilities and costs differently between buyer and seller, impacting overall expenditure.
Strategic Buyer Tips for International B2B Procurement
-
Negotiate Based on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Focus beyond unit price—consider dressing longevity, frequency of change, and patient outcomes. Higher upfront costs may yield savings by reducing dressing changes and complications. -
Leverage Volume Consolidation
Collaborate with regional healthcare networks or distributors to aggregate demand, unlocking better pricing tiers and reducing freight costs. -
Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Quality Assurance
Prioritize suppliers with recognized certifications to avoid risks of substandard products, which can lead to increased healthcare costs and liability. -
Factor in Import Duties and Regulatory Compliance
Understand local import regulations and associated taxes. Partnering with suppliers familiar with your market can streamline customs clearance and reduce delays. -
Consider Incoterm Implications
Opt for terms that balance cost control and risk management. For example, CIF may be preferable for buyers lacking logistics infrastructure, whereas FOB can offer more control and potential savings for experienced importers. -
Assess Packaging and Shelf Life
Choose dressings with optimal shelf life and packaging suited for local climate conditions to minimize waste and inventory losses.
Pricing Disclaimer
Prices for Optifoam dressings vary significantly based on region, order volume, supplier, and product variant. The insights provided are indicative and intended to guide negotiation and sourcing decisions rather than serve as fixed price references. Buyers should engage directly with manufacturers or authorized distributors for precise quotations tailored to their procurement needs.
By thoroughly understanding these cost components and pricing factors, international B2B buyers can strategically source Optifoam dressings that align with budget constraints and clinical requirements, ultimately enhancing wound care quality across diverse healthcare settings.
Spotlight on Potential optifoam dressing Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section offers a look at a few manufacturers active in the ‘optifoam dressing’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct their own extensive due diligence before any engagement. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for optifoam dressing
Critical Technical Properties of Optifoam Dressings
When sourcing optifoam dressings, understanding key technical specifications is crucial for ensuring product effectiveness, compliance, and suitability for your healthcare market. Below are the essential properties that international B2B buyers should consider:
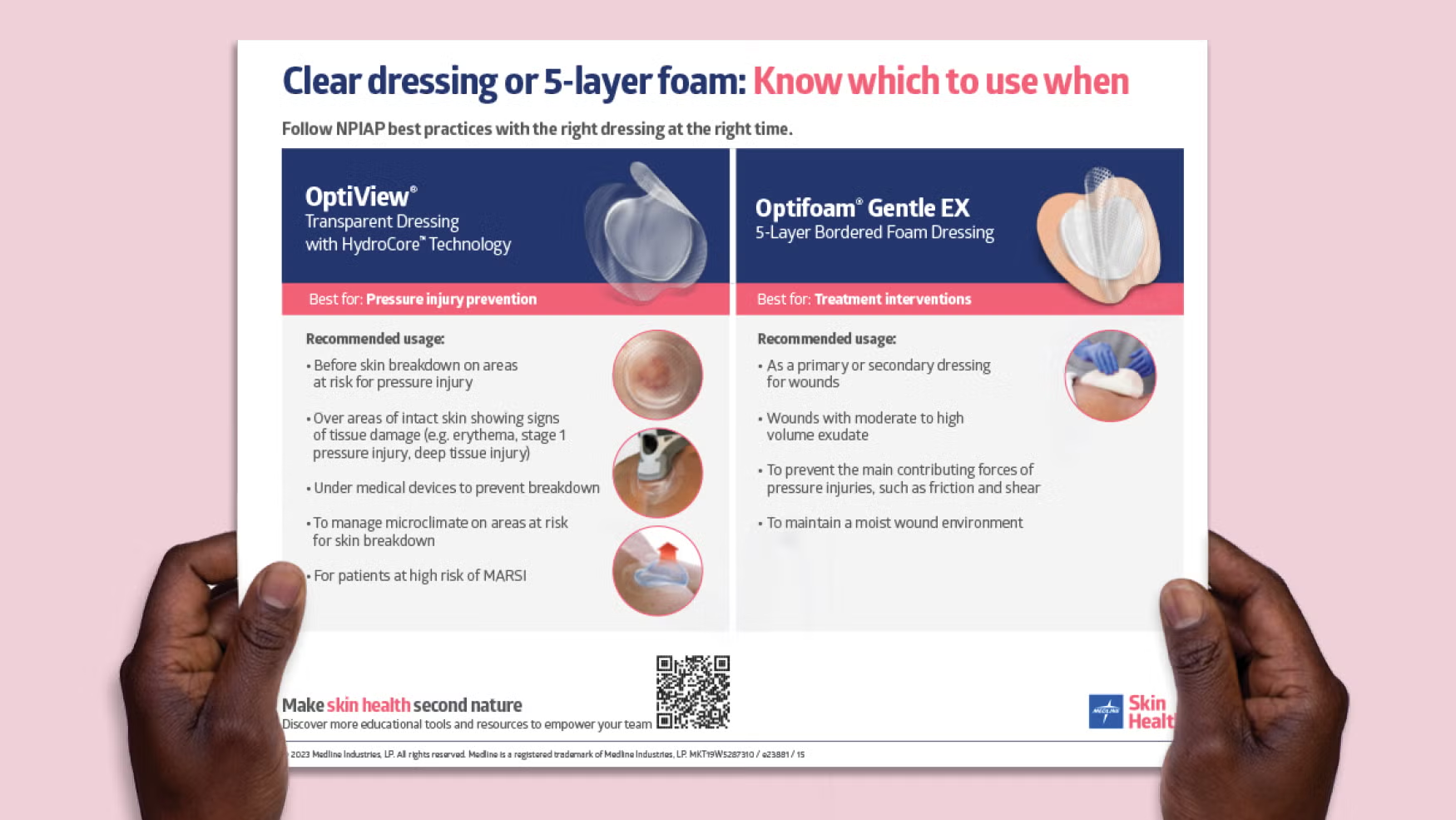
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Material Composition and Grade
Optifoam dressings are primarily made from medical-grade polyurethane foam combined with a silicone adhesive border. The foam’s quality impacts absorbency, cushioning, and breathability, while the silicone border ensures gentle adhesion without skin trauma. For buyers, verifying medical-grade certification guarantees safety and regulatory compliance, especially important in markets with strict healthcare standards such as Europe and the Middle East. -
Moisture Vapor Transmission Rate (MVTR)
MVTR measures the dressing’s ability to allow moisture vapor to escape while maintaining a moist wound environment. Optifoam’s MVTR adapts to fluid levels, balancing breathability and moisture retention to promote optimal healing. For purchasers, understanding MVTR helps match dressings to wound types and climates—critical for humid regions in Africa or dry areas in parts of South America. -
Adhesive Technology and Reusability
The silicone adhesive border offers gentle yet secure adhesion, minimizing pain during dressing changes. Importantly, this adhesive allows the dressing to be lifted and reapplied without losing stickiness. For B2B buyers, this feature can reduce product waste and improve patient comfort, making it attractive for healthcare providers focused on cost efficiency and quality care. -
Absorbency Capacity and Drainage Management
Optifoam dressings are designed to manage moderate to heavy exudate effectively, protecting surrounding skin from maceration. Absorbency ratings help buyers select appropriate products for wound severity and type. This property is vital in environments where dressing change frequency must be optimized due to limited healthcare resources. -
Dimensions and Packaging Specifications
Dressings come in various sizes tailored for different wound locations (e.g., sacrum, limbs). Accurate sizing reduces waste and ensures better wound coverage. Additionally, understanding packaging details such as unit count per box or case (e.g., 50 units per carton) aids in inventory planning and logistics, especially for importers managing supply chains across continents. -
Shelf Life and Storage Conditions
Optifoam dressings typically offer a shelf life of 2-3 years under recommended storage conditions. Buyers must assess shelf life to avoid stock obsolescence, particularly when importing large quantities to regions with variable demand cycles or storage capabilities.
Key Trade Terminology for International B2B Buyers
Navigating international trade requires familiarity with common industry terms to streamline procurement and contractual processes. Here are essential terms for B2B buyers of optifoam dressings:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to a company that produces products or components sold by another company under its brand. In wound care, OEM arrangements might allow buyers to source optifoam dressings branded with their own label, enabling local market customization and brand differentiation. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest quantity a supplier is willing to sell per order. Understanding MOQ is critical for buyers in emerging markets like Nigeria or Saudi Arabia, where capital constraints or storage limitations may restrict large purchases. Negotiating MOQs can facilitate market entry or trial orders. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products and quantities. RFQs are essential for comparing offers from multiple manufacturers or distributors, helping buyers secure competitive pricing and favorable contract conditions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce defining the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and customs clearance. Common terms include FOB (Free on Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight). Selecting appropriate Incoterms impacts total landed cost and risk management, crucial for cross-border shipments. -
Lead Time
The period between placing an order and receiving the goods. For optifoam dressings, lead times affect inventory planning and continuity of care in healthcare facilities. Buyers should confirm lead times upfront to avoid stockouts, especially when supply chains face disruption risks. -
Batch/Lot Number
A unique identifier assigned to a specific production run. Batch numbers facilitate traceability for quality control and regulatory compliance, enabling buyers to track product history and manage recalls if necessary.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed procurement decisions that optimize product performance, cost efficiency, and supply chain reliability in diverse healthcare markets.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the optifoam dressing Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global market for optifoam dressings is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising incidences of chronic wounds, pressure ulcers, and diabetic foot ulcers worldwide. This demand is particularly pronounced in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where expanding healthcare infrastructure and increasing awareness of advanced wound care solutions are catalyzing procurement activities. For B2B buyers in countries like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia, the focus is on sourcing products that combine clinical efficacy with cost-efficiency to address diverse patient needs across public and private healthcare sectors.
Key market dynamics include heightened adoption of multilayer foam dressings like Optifoam, which offer superior moisture management, cushioning, and protection against infection. Innovations such as silicone adhesive borders that allow for gentle, re-positionable application are gaining traction, reducing trauma during dressing changes—a critical factor in patient compliance and wound healing outcomes. Additionally, the integration of digital supply chain platforms and telehealth-enabled ordering is streamlining procurement processes, enabling buyers to efficiently manage inventory and respond to fluctuating demand.
Emerging sourcing trends emphasize regional partnerships with manufacturers who can ensure reliable delivery timelines and localized product support. For African and South American markets, this often means engaging with distributors that understand the regulatory and logistical complexities unique to these regions. In Europe and the Middle East, buyers are increasingly prioritizing products backed by robust clinical evidence and certifications, reflecting stringent healthcare standards and reimbursement frameworks. Furthermore, digital marketplaces and B2B e-procurement solutions are becoming integral, facilitating transparent pricing and bulk order management for healthcare institutions.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a critical consideration for international buyers of optifoam dressings, reflecting broader healthcare sector commitments to reducing environmental footprints. Foam dressings, while highly effective, traditionally involve synthetic materials that pose challenges for biodegradability and waste management. Consequently, B2B buyers are placing greater emphasis on sourcing from manufacturers that prioritize sustainable production methods, such as using recyclable packaging and reducing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in manufacturing.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, with buyers seeking supply chains that ensure labor rights compliance and promote fair trade practices. This is especially relevant for multinational buyers operating across Africa, the Middle East, and South America, where supply chain transparency can vary significantly. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 13485 (Medical Device Quality Management) serve as trusted benchmarks indicating a manufacturer’s commitment to sustainability and quality.
Moreover, the rising demand for “green” wound care products has prompted some manufacturers to explore biocompatible and partially bio-based foam materials that reduce environmental impact without compromising dressing performance. Buyers should assess suppliers’ sustainability reports and request lifecycle analyses to verify claims. Partnering with suppliers who actively engage in circular economy initiatives—such as take-back programs or waste reduction schemes—can enhance corporate social responsibility profiles and align with increasingly stringent procurement policies in Europe and the Middle East.
Evolution and Historical Context
The evolution of foam dressings like Optifoam reflects significant advances in wound care technology over the past two decades. Initially, foam dressings were developed to provide a moist wound healing environment superior to traditional gauze, enhancing healing rates and patient comfort. Over time, innovations such as adhesive silicone borders and multilayer constructions have improved ease of use and extended wear times, reducing dressing change frequency and associated healthcare costs.
For B2B buyers, understanding this progression is vital, as it highlights the shift from basic wound coverings to sophisticated, evidence-based medical devices that support complex wound management protocols. The increasing clinical validation of foam dressings has propelled their adoption in diverse healthcare settings, from acute hospitals to home care, making them a staple in modern wound care procurement portfolios. This historical context underscores the importance of selecting products that align with the latest clinical guidelines and technological standards to optimize patient outcomes and operational efficiency.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of optifoam dressing
-
How can international B2B buyers verify the credibility of optifoam dressing suppliers?
To ensure supplier credibility, buyers should request certifications such as ISO 13485 (medical device quality management) and CE marking for European compliance. Checking FDA approvals or equivalent regulatory clearances is crucial for product legitimacy. Additionally, conduct due diligence by reviewing supplier history, requesting client references, and verifying manufacturing facilities via virtual tours or third-party audits. Engaging with suppliers who provide transparent product documentation and sample testing further reduces risk in international procurement, especially in regions like Africa and the Middle East where regulatory frameworks may vary. -
Is customization of optifoam dressings available to meet specific clinical or regional requirements?
Many manufacturers offer customization options including dressing size, adhesive type (e.g., silicone border for gentle adhesion), and packaging formats. Buyers should discuss specific wound care needs or regional preferences with suppliers early in negotiations. Customization may include sterile packaging adaptations or labeling in local languages, which are critical for regulatory acceptance in markets like Nigeria or Saudi Arabia. Confirm minimum order quantities (MOQs) for customized products, as they might be higher than standard stock items, and evaluate lead times accordingly. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for bulk orders of optifoam dressings?
MOQs vary by supplier but generally range from 50 to 500 units per SKU, depending on customization and packaging requirements. Lead times typically span 4 to 8 weeks for standard products, extending to 10-12 weeks if customization or regulatory documentation is involved. Buyers should negotiate clear timelines and consider buffer periods for shipping and customs clearance, especially when importing into countries with complex regulatory environments such as South American nations or the Middle East. Early planning helps avoid stockouts and ensures continuous supply. -
What payment terms are common for international B2B purchases of optifoam dressings?
Suppliers often request a combination of upfront payment and balance upon shipment or delivery. Common terms include 30% deposit with order confirmation and 70% before shipment, or net 30-60 days post-invoice for established buyers. Letters of credit (LC) and escrow services are recommended to mitigate payment risks, particularly in new international partnerships. Buyers should confirm currency options, bank charges, and possible trade finance support available in their country to streamline transactions. -
Which quality assurance certifications and standards should buyers look for in optifoam dressing suppliers?
Key certifications include ISO 13485 for medical device manufacturing, CE marking for compliance with European Medical Device Regulation (MDR), and FDA clearance for the US market. Additionally, compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and documented biocompatibility testing are essential. Buyers should request product technical data sheets, batch testing reports, and shelf-life information to ensure consistent quality. For markets like Europe and the Middle East, confirming adherence to local regulatory requirements is critical to avoid import delays. -
What logistical considerations should international buyers keep in mind when importing optifoam dressings?
Optifoam dressings are typically non-hazardous but require protection from extreme temperatures and moisture during transit. Choosing suppliers with experience in international shipping and customs documentation is vital. Buyers should clarify Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) to understand responsibility for freight and insurance. Warehousing facilities in destination countries should maintain appropriate storage conditions. For regions with limited cold chain infrastructure, selecting foam dressings with robust packaging and longer shelf lives reduces product degradation risks. -
How should disputes regarding product quality or delivery be managed in international optifoam dressing contracts?
Contracts should clearly define quality standards, inspection procedures, and remedies for non-compliance. Including clauses for third-party inspection or arbitration helps resolve disputes impartially. Buyers must document all communications, inspect shipments promptly upon arrival, and report issues within agreed timeframes. Establishing a relationship with suppliers who offer responsive customer service and warranty coverage can facilitate amicable resolutions. In cross-border scenarios, understanding local legal frameworks and international trade laws is essential. -
Are there specific regulatory challenges for importing optifoam dressings into African, South American, or Middle Eastern markets?
Yes, regulatory requirements differ widely across these regions. For example, the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) mandates conformity with the Gulf Medical Device Regulation, while Brazil requires ANVISA registration. African countries may have varying degrees of regulatory oversight, often requiring local agent representation or additional testing. Buyers should engage regulatory consultants or local partners to navigate approvals efficiently. Proper documentation, including product dossiers, certificates of free sale, and labeling compliance, is critical to avoid shipment delays and ensure market access.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for optifoam dressing
Strategic sourcing of Optifoam dressings presents a compelling opportunity for international B2B buyers seeking advanced wound care solutions. Key advantages include the product’s versatility across various wound types, its patient-friendly features such as gentle silicone adhesion and moisture management, and its proven efficacy in pressure injury prevention. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate reliability, regulatory compliance, and robust supply chain capabilities will mitigate risks and ensure timely delivery.
Critical considerations for strategic procurement include:
– Supplier vetting: Evaluate manufacturers and distributors based on product certifications, quality assurance, and after-sales support.
– Cost-efficiency: Balance price competitiveness with product performance to optimize value over the product lifecycle.
– Customization and availability: Seek partners offering diverse dressing sizes and types to meet varied clinical needs.
– Regulatory alignment: Ensure compliance with local medical device regulations to streamline import and usage approvals.
Looking ahead, the growing emphasis on patient-centered wound care and evolving healthcare infrastructures in emerging markets will drive increased demand for innovative foam dressings like Optifoam. Buyers are encouraged to engage in collaborative partnerships with manufacturers to leverage bulk purchasing, localized training, and digital health integration. This proactive approach will not only enhance clinical outcomes but also secure a competitive advantage in the dynamic global wound care market.