Definitive Guide to Silver Alginate Dressing for B2B Buyers
Guide to Silver Alginate Dressing
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for silver alginate dressing
- Understanding silver alginate dressing Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of silver alginate dressing
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for silver alginate dressing
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for silver alginate dressing
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for silver alginate dressing Sourcing
- Spotlight on Potential silver alginate dressing Manufacturers and Suppliers
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for silver alginate dressing
- Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the silver alginate dressing Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of silver alginate dressing
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for silver alginate dressing
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for silver alginate dressing
Silver alginate dressings have emerged as a critical innovation in advanced wound care, combining the superior absorbency of alginate fibers with the potent antimicrobial properties of silver. This unique synergy addresses the complex needs of wounds with moderate to heavy exudate, reducing infection risks while promoting faster healing. For B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Indonesia and Brazil—understanding the nuances of this product is essential to meet growing healthcare demands and regulatory standards.
This comprehensive guide offers an in-depth exploration of silver alginate dressings, empowering international buyers to make informed sourcing decisions. It covers a broad spectrum of topics, including:
- Types of silver alginate dressings tailored to diverse wound care requirements
- Material composition and manufacturing processes ensuring quality and efficacy
- Quality control protocols vital for compliance and patient safety
- Global supplier landscape and market trends, highlighting opportunities and challenges
- Cost analysis and procurement strategies to optimize budget and supply chain efficiency
- Frequently asked questions addressing common concerns and technical details
By leveraging this knowledge, healthcare distributors, medical suppliers, and procurement specialists can confidently navigate the global marketplace. The guide equips buyers with actionable insights to identify reputable manufacturers, evaluate product performance, and align purchases with local healthcare regulations. Ultimately, it supports the delivery of superior wound care solutions that enhance patient outcomes while driving sustainable business growth in diverse international markets.
Understanding silver alginate dressing Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Silver Alginate | Combines alginate fibers with silver ions; gel-forming | Chronic wounds, ulcers, moderate to heavy exudate wounds | Pros: High absorbency, antimicrobial; Cons: May require frequent changes in very heavy exudate cases |
| Silver Alginate with Foam Backing | Alginate-silver layer with an added foam backing for cushioning and extra absorption | Surgical wounds, burns, trauma wounds | Pros: Enhanced protection and absorption; Cons: Higher cost, bulkier dressing |
| Silver Alginate Rope | Rope or strand form for packing deep or tunneling wounds | Deep wounds, cavity wounds, tunneling ulcers | Pros: Flexible for irregular wounds, effective antimicrobial action; Cons: Requires skilled application |
| Silver Alginate Sheet with Adhesive Border | Alginate-silver sheet combined with adhesive border for secure placement | Post-operative wounds, mobile patients | Pros: Easy application, secure fit; Cons: Adhesive may cause skin irritation in sensitive patients |
| Silver Alginate with Additional Hydrofiber Layer | Incorporates a hydrofiber layer to increase fluid retention capacity | Highly exuding wounds, diabetic foot ulcers | Pros: Superior fluid handling, reduced leakage; Cons: Premium pricing, may be less breathable |
Standard Silver Alginate
This is the most common form, integrating alginate fibers with silver ions to form a gel upon contact with wound exudate. It is highly effective for moderate to heavily exuding chronic wounds such as pressure ulcers and venous leg ulcers. For B2B buyers, this type offers a balance of antimicrobial protection and absorbency at a competitive price point. Buyers should consider supply consistency and dressing change frequency based on wound exudate levels.
Silver Alginate with Foam Backing
These dressings combine the antimicrobial and absorbent properties of silver alginate with a foam backing that provides cushioning and additional fluid absorption. This type is ideal for acute wounds such as burns and surgical sites that require both protection and comfort. B2B purchasers should evaluate the cost implications and storage requirements, as these dressings tend to be bulkier and priced higher than standard types.
Silver Alginate Rope
Designed in a rope or strand form, this variant is specifically suited for deep, tunneling, or cavity wounds where a flat dressing cannot effectively cover the wound bed. Its flexibility allows for precise packing and sustained antimicrobial action within complex wound geometries. Buyers need to ensure availability of trained healthcare professionals for proper application and consider packaging sizes that match wound care protocols.
Silver Alginate Sheet with Adhesive Border
This dressing includes an adhesive border that secures the alginate-silver sheet firmly in place, reducing the risk of displacement. It is particularly beneficial for post-operative wounds or patients with high mobility. For B2B buyers, the adhesive feature simplifies application and reduces labor time but may require careful selection to avoid skin irritation in sensitive populations. Shelf life and adhesive strength are critical purchase considerations.
Silver Alginate with Additional Hydrofiber Layer
By integrating a hydrofiber layer, this type enhances fluid retention beyond standard alginate capabilities, making it suitable for wounds with very high exudate, such as diabetic foot ulcers. This advanced dressing minimizes leakage and maceration, promoting a cleaner wound environment. Buyers should weigh the premium cost against the clinical benefits and assess compatibility with existing wound care protocols and budgets.
Related Video: Oxymax Silver Alginate Dressing- How to apply on the wound
Key Industrial Applications of silver alginate dressing
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of silver alginate dressing | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare & Hospitals | Management of chronic wounds and post-surgical sites | Accelerates healing, reduces infection rates, lowers hospital stay duration | Certification compliance (ISO, CE), consistent antimicrobial efficacy, bulk supply reliability |
| Medical Device Manufacturers | Incorporation in advanced wound care kits and products | Enhances product portfolio with antimicrobial and absorbent features | Quality assurance, regulatory approvals, compatibility with product design |
| Elderly Care & Long-term Care Facilities | Treatment of pressure ulcers and diabetic foot ulcers | Improves patient outcomes, reduces complications and re-admissions | Cost-effectiveness, ease of application, availability of various sizes |
| Military & Emergency Medical Services (EMS) | Field wound management for trauma and burns | Rapid infection control, effective exudate management in austere conditions | Durability, shelf life, ease of transport and application under field conditions |
| Veterinary Medicine | Treatment of animal wounds, especially infected or exuding wounds | Promotes faster healing, prevents cross-contamination | Animal-safe formulations, supplier reliability, packaging suitable for veterinary use |
Healthcare & Hospitals
In hospitals and clinical settings across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, silver alginate dressings are indispensable for managing chronic wounds such as diabetic foot ulcers and venous leg ulcers, as well as post-surgical wounds prone to infection. These dressings’ dual-action antimicrobial and absorbent properties help reduce bacterial load while maintaining an optimal moist environment, promoting faster healing and reducing the length of hospital stays. For international B2B buyers, it is crucial to source dressings that meet international certifications (ISO, CE) and ensure consistent silver ion release for reliable antimicrobial performance.
Medical Device Manufacturers
Manufacturers of advanced wound care products incorporate silver alginate dressings into kits designed for surgical aftercare or chronic wound management. The integration of these dressings enhances product portfolios by offering superior infection control and fluid management. Buyers from emerging markets like Brazil and Indonesia should prioritize suppliers who provide rigorous quality assurance and regulatory documentation to facilitate smooth market entry and compliance with local health authorities.
Elderly Care & Long-term Care Facilities
Pressure ulcers and diabetic foot ulcers are common in elderly populations, especially in long-term care facilities. Silver alginate dressings offer effective management by absorbing heavy exudate and preventing infection, which reduces complications and hospital readmissions. For B2B buyers in regions with aging populations, sourcing cost-effective, easy-to-apply dressings in multiple sizes is key to improving patient care while managing operational costs.
Military & Emergency Medical Services (EMS)
In military and emergency medical contexts, wounds from trauma or burns require rapid, reliable care to prevent infection and manage exudate in challenging environments. Silver alginate dressings provide these benefits with durable, easy-to-apply materials that maintain antimicrobial action even in austere conditions. Buyers should focus on products with extended shelf life, compact packaging for transport, and certifications ensuring performance under extreme conditions.
Veterinary Medicine
Veterinary clinics and animal care facilities utilize silver alginate dressings to treat infected or heavily exuding wounds in animals, preventing cross-contamination and promoting healing. International buyers must ensure the dressings are safe for animal use and sourced from suppliers with proven reliability and appropriate packaging for veterinary applications, particularly in markets with growing pet care industries like the Middle East and South America.
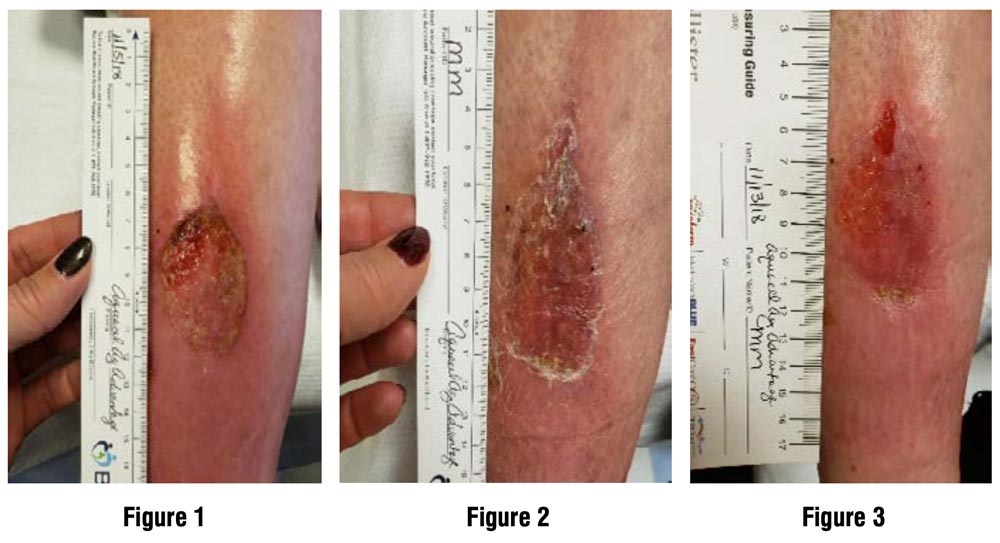
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Strategic Material Selection Guide for silver alginate dressing
When selecting materials for silver alginate dressings, B2B buyers must consider factors such as absorbency, antimicrobial efficacy, biocompatibility, manufacturing complexity, and regulatory compliance. The choice of base materials and additives directly impacts product performance, cost, and suitability for diverse international markets, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Below is an analysis of four common material components used in silver alginate dressings, focusing on their properties and implications for global buyers.
1. Alginate Fiber (Derived from Brown Seaweed)
Key Properties:
Alginate fibers are highly absorbent polysaccharides extracted from brown seaweed. They can absorb up to 20 times their weight in fluid and form a gel upon contact with wound exudate, maintaining a moist environment essential for healing. Alginate is naturally biodegradable and biocompatible, which minimizes allergic reactions.
Pros:
– Excellent exudate management due to gel formation.
– Promotes autolytic debridement and supports faster healing.
– Renewable and sustainable source, appealing in eco-conscious markets.
– Compatible with silver ion integration for antimicrobial action.
Cons:
– Quality and purity can vary depending on seaweed source and extraction process.
– Sensitive to storage conditions; moisture exposure before use can degrade performance.
– Manufacturing requires precise control to maintain fiber integrity.
Impact on Application:
Ideal for wounds with moderate to heavy exudate, such as diabetic foot ulcers and pressure sores. Alginate’s natural origin makes it favorable in markets emphasizing organic or natural healthcare products.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in Africa and South America should verify alginate sourcing and certification to ensure consistent quality. Compliance with ISO 10993 for biocompatibility and regional standards like the European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.) is critical for buyers in Europe and the Middle East. Suppliers offering traceability and sustainable harvesting practices are preferred in environmentally regulated markets like the EU.
2. Silver Ions (Antimicrobial Agent)
Key Properties:
Silver ions provide broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity by disrupting bacterial cell membranes and inhibiting microbial replication. Incorporated into alginate fibers, silver is released gradually in the presence of wound exudate, ensuring sustained antimicrobial protection.
Pros:
– Effective against bacteria, fungi, and some viruses, reducing infection risk.
– Sustained release mechanism prolongs dressing efficacy.
– Enhances wound healing by maintaining a clean wound bed.
Cons:
– Higher material cost compared to non-silver dressings.
– Potential for silver ion cytotoxicity if concentration is not optimized.
– Regulatory scrutiny varies by region due to silver’s antimicrobial claims.
Impact on Application:
Crucial for wounds at high risk of infection or already infected, such as surgical wounds or chronic ulcers. Silver’s antimicrobial properties are particularly valuable in tropical climates prevalent in Africa and South America, where infection rates are higher.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers must ensure that silver content complies with local regulations, such as the EU’s Medical Device Regulation (MDR) or Brazil’s ANVISA standards. Certifications like ASTM E2149 for antimicrobial efficacy testing can support procurement decisions. The Middle East market often requires halal certification for wound care products, which may affect silver sourcing and processing.
3. Non-Woven Carrier Fabric (Support Layer)
Key Properties:
Non-woven fabrics, often made from polyester or rayon, provide structural support to the alginate-silver composite. They facilitate easy handling, conformability to wound contours, and breathability.
Pros:
– Lightweight and flexible, enhancing patient comfort.
– Allows for efficient fluid transfer to the alginate layer.
– Cost-effective and scalable for mass production.
Cons:
– Synthetic fibers may have lower biodegradability compared to natural fibers.
– Potential for linting or fiber shedding if not properly processed.
– Some materials may cause skin irritation in sensitive patients.
Impact on Application:
Ideal for dressings requiring flexibility and durability, such as those used on joints or mobile body parts. The carrier fabric’s breathability supports moisture vapor transmission, preventing maceration.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should look for compliance with OEKO-TEX® standards or equivalent certifications to ensure skin safety. In regions like Indonesia and Brazil, sourcing locally produced non-woven fabrics can reduce costs and lead times but requires verification of quality standards such as ISO 9001.
4. Cross-Linking Agents (e.g., Calcium Salts)
Key Properties:
Calcium ions are commonly used to cross-link alginate fibers, enhancing gel strength and stability. This improves the dressing’s mechanical integrity during use and controls the rate of gel formation.
Pros:
– Improves dressing durability and handling during application and removal.
– Enhances hemostatic properties, beneficial for bleeding wounds.
– Generally low-cost additive.
Cons:
– Excessive cross-linking can reduce absorbency and flexibility.
– Variability in cross-linker purity can affect dressing consistency.
– May interact with silver ions, potentially affecting antimicrobial release.
Impact on Application:
Cross-linked alginate dressings are suited for wounds requiring moderate mechanical protection and controlled moisture retention. They are effective in surgical and trauma wound care.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with pharmacopeial standards (USP, Ph. Eur.) for calcium salts is important for buyers in regulated markets like Europe. In emerging markets such as Africa and South America, buyers should assess supplier quality control to avoid batch variability. Cross-linking agents should be compatible with silver formulations to maintain antimicrobial efficacy.
| Material | Typical Use Case for silver alginate dressing | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alginate Fiber | Absorbent layer for moderate to heavy exudate wounds | High absorbency and biocompatibility | Quality varies by source; sensitive to moisture | Medium |
| Silver Ions | Antimicrobial component for infected or high-risk wounds | Broad-spectrum antimicrobial, sustained release | Higher cost; regulatory complexity | High |
| Non-Woven Carrier Fabric | Structural support and dressing flexibility | Lightweight, breathable, cost-effective | Potential skin irritation; synthetic origin | Low to Medium |
| Cross-Linking Agents | Gel strength enhancer and hemostatic aid | Improves durability and handling | May reduce absorbency if overused; purity issues | Low |
This material
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for silver alginate dressing
Manufacturing Process of Silver Alginate Dressings
Silver alginate dressings are advanced wound care products requiring precise and controlled manufacturing processes to ensure their efficacy and safety. The typical production involves several key stages:
1. Raw Material Preparation
- Alginate Extraction and Purification: Alginate is derived from brown seaweed and must be purified to medical-grade standards. This involves washing, drying, and milling to obtain uniform alginate powder or fibers.
- Silver Compound Preparation: Silver is commonly incorporated as silver ions or nanoparticles. The silver source must meet strict purity criteria to ensure antimicrobial effectiveness without toxicity.
- Quality Verification of Inputs: Before production, raw materials undergo incoming quality control (IQC) tests such as purity, particle size, and microbial contamination to ensure compliance with specifications.
2. Dressing Formation
- Alginate Fiber Formation: Alginate fibers or sheets are formed by processes like wet spinning or extrusion, which align and solidify the alginate structure.
- Silver Integration: The silver ions or nanoparticles are uniformly incorporated into the alginate matrix through impregnation or co-extrusion methods. Uniform distribution is critical for consistent antimicrobial activity.
- Crosslinking and Gelation Control: Chemical or ionic crosslinking agents may be applied to stabilize the alginate fibers and control their gel-forming behavior on wound contact.
3. Assembly and Layering
- Multi-layer Construction: Silver alginate dressings often include additional layers such as non-woven backing or absorbent pads to enhance mechanical strength and absorption capacity.
- Cutting and Shaping: The composite material is cut into various sizes and shapes tailored for different wound applications. Automated precision cutting ensures uniformity and reduces waste.
- Sterilization Preparation: Dressings are packaged in a manner compatible with sterilization methods (e.g., ethylene oxide, gamma irradiation) without compromising dressing integrity.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
4. Finishing and Packaging
- Sterilization: Final sterilization is conducted to eliminate microbial contaminants, critical for wound care products.
- Quality Labeling and Packaging: Dressings are sealed in sterile packaging with clear labeling including batch numbers, expiry dates, and usage instructions. Packaging materials protect against moisture and contamination during storage and transport.
- Batch Documentation: Comprehensive manufacturing records and batch traceability documents are prepared for regulatory compliance and quality audits.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Quality Assurance and Control (QA/QC) Framework
For B2B buyers sourcing silver alginate dressings internationally, understanding the quality assurance framework is essential to ensure product safety, performance, and regulatory compliance.
Relevant International and Industry Standards
- ISO 9001: The foundational quality management system standard ensuring consistent manufacturing and continuous improvement.
- ISO 13485: Specific to medical devices, including wound dressings, this standard mandates stringent controls over design, production, and post-market surveillance.
- CE Marking (Europe): Indicates conformity with EU medical device regulations, crucial for buyers in Europe and many other markets recognizing CE.
- FDA and ANVISA Approvals: For markets like the USA and Brazil, compliance with FDA or ANVISA regulatory requirements is often necessary.
- Other Certifications: Depending on the destination market, certifications such as TGA (Australia), PMDA (Japan), or Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) medical device conformity may be required.
Quality Control Checkpoints
| Stage | Key QC Activities | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Incoming QC (IQC) | Raw material identity, purity, microbiology | Ensure inputs meet specification before use |
| In-Process QC (IPQC) | Alginate fiber properties, silver content uniformity, moisture level, dimensional accuracy | Detect defects early during production |
| Final QC (FQC) | Sterility testing, absorbency, tensile strength, antimicrobial efficacy, packaging integrity | Confirm finished product quality and safety |
Common Testing Methods
- Sterility Tests: Validated microbiological assays confirm absence of viable contaminants.
- Silver Ion Release and Content: Analytical methods (e.g., ICP-MS) quantify silver concentration to verify antimicrobial potential.
- Absorbency and Gel Formation: Standardized fluid absorption tests ensure dressings meet performance criteria for exudate management.
- Mechanical Testing: Tensile strength and flexibility tests confirm durability during application.
- Biocompatibility Assessments: Cytotoxicity and irritation tests ensure patient safety.
Verifying Supplier Quality: Practical Steps for B2B Buyers
International B2B buyers should adopt a proactive approach to quality verification to mitigate supply risks and ensure regulatory compliance.
Supplier Audits
- Conduct on-site audits focused on manufacturing processes, hygiene controls, sterilization practices, and documentation systems.
- Evaluate supplier compliance with ISO 13485 and other relevant certifications.
- Review raw material sourcing and traceability to confirm sustainable and quality inputs.
Documentation and Reports
- Request detailed Certificates of Analysis (CoA) for each batch, including test results for silver content, sterility, and absorbency.
- Obtain Device Master Records (DMR) or equivalent manufacturing process documentation.
- Verify sterilization validation reports and shelf-life stability data.
Third-Party Inspection and Testing
- Utilize independent laboratories for batch verification testing, especially for antimicrobial efficacy and biocompatibility.
- Engage third-party inspection agencies for pre-shipment inspections to confirm packaging integrity and labeling compliance.
Quality Assurance Nuances for Buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe
- Regulatory Landscape Variability: Markets such as Brazil (ANVISA) and the European Union (MDR) have stringent regulations requiring documented compliance. In contrast, some African and Middle Eastern countries may have evolving or less harmonized frameworks, necessitating extra diligence.
- Import and Certification Requirements: Buyers in these regions should verify if local authorities require additional certifications or registration before import. For example, Brazil mandates ANVISA registration for medical devices, while many African countries require WHO prequalification or local health authority approval.
- Climate and Storage Considerations: High humidity and temperature prevalent in parts of Africa and South America can impact product shelf life. Buyers should confirm that packaging and storage recommendations are suitable for their specific environments.
- Supplier Transparency and Communication: Language barriers and time zone differences may affect supplier responsiveness. Prioritize suppliers with multilingual support and clear quality communication channels.
- Cost vs. Quality Balance: While competitive pricing is important, avoid compromising on quality certifications and testing rigor. Investing in verified quality reduces risks of product recalls, regulatory fines, and patient safety issues.
Summary for International B2B Buyers
- Silver alginate dressings require complex manufacturing involving precise alginate processing, silver integration, and sterilization.
- Adherence to ISO 13485, CE marking, and local regulatory approvals is critical for quality assurance.
- Robust IQC, IPQC, and FQC checkpoints, along with validated testing methods, ensure consistent product performance.
- Buyers should engage in supplier audits, review detailed documentation, and leverage third-party testing to verify quality.
- Understanding regional regulatory nuances, environmental factors, and supply chain transparency is key to successful sourcing in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
By applying these insights, international B2B buyers can confidently select silver alginate dressing suppliers who meet the highest quality and regulatory standards, ensuring safe and effective wound care solutions for their markets.
Related Video: Our manufacturing process: Textiles
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for silver alginate dressing Sourcing
Understanding the cost and pricing dynamics of silver alginate dressings is critical for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize procurement strategies across diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis breaks down key cost components, price influencers, and actionable tips to enhance cost-efficiency and value.
Key Cost Components in Silver Alginate Dressing Production
-
Raw Materials:
The primary costs stem from sourcing high-quality alginate (derived from brown seaweed) and pharmaceutical-grade silver compounds. The purity and antimicrobial efficacy of silver significantly affect material expenses. Suppliers with sustainable alginate sourcing or proprietary silver integration technologies may command premium prices. -
Labor and Manufacturing Overhead:
Skilled labor is required for precision manufacturing to ensure consistent dressing quality, including processes like fiber impregnation with silver ions and sterile packaging. Overhead costs include facility maintenance, utilities, and compliance with medical device manufacturing standards (e.g., ISO 13485). -
Tooling and Equipment:
Specialized machinery for alginate fiber processing, silver ion embedding, and quality control testing adds upfront and maintenance costs. Custom tooling for specific dressing sizes or shapes can increase initial expenses but may reduce per-unit costs at higher volumes. -
Quality Control (QC):
Rigorous QC protocols are essential to meet international medical device regulations, including antimicrobial efficacy testing, sterility assurance, and biocompatibility assessments. These steps add to the overall cost but are vital for product acceptance in regulated markets. -
Logistics and Distribution:
Shipping costs vary widely depending on the buyer’s location. For regions like Africa and South America, additional costs may arise from longer transit times, customs clearance, and local distribution challenges. Cold-chain logistics are generally not required, but secure packaging to prevent contamination is necessary. -
Supplier Margin:
Manufacturers and distributors build margins based on market positioning, volume discounts, and competitive landscape. Premium brands with clinically proven efficacy or certifications might have higher margins justified by added value.
Influencing Factors on Pricing
-
Order Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ):
Larger purchase volumes typically reduce the unit price due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs carefully, balancing inventory costs with price benefits. -
Product Specifications and Customization:
Custom sizes, thicknesses, or integration of additional features (e.g., enhanced silver release profiles) can increase costs. Standardized products usually offer better pricing and faster delivery. -
Material Quality and Certifications:
Dressings compliant with CE marking, FDA approval, or equivalent certifications command higher prices but ensure regulatory acceptance in target markets, reducing downstream costs. -
Supplier Reputation and Capabilities:
Established suppliers with proven track records, robust supply chains, and after-sales support may price higher but offer reliability and reduced risk. -
Incoterms and Delivery Terms:
Pricing varies significantly based on Incoterms such as FOB, CIF, or DDP. Buyers must understand who bears shipping, insurance, and customs duties to accurately calculate landed cost.
Strategic Buyer Tips for International Procurement
-
Negotiate Beyond Price:
Engage suppliers on payment terms, lead times, and volume discounts. For emerging markets like Indonesia or Brazil, flexible terms can offset higher freight or tariff costs. -
Calculate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO):
Consider not just unit price but also storage, handling, potential wastage, and regulatory compliance costs. A slightly higher-priced dressing with better shelf life or efficacy may reduce overall treatment costs. -
Leverage Local Distribution Networks:
Partnering with regional distributors can lower last-mile logistics expenses and improve supply chain responsiveness, especially in Africa and the Middle East. -
Assess Pricing Nuances by Region:
Import duties, taxes, and local regulatory fees vary by country. Buyers should work with customs experts to anticipate these charges and factor them into procurement budgets. -
Request Samples and Conduct Pilot Runs:
Testing product performance and supplier reliability before committing to large orders mitigates risk and supports better negotiation leverage. -
Stay Informed on Market Trends:
Fluctuations in raw material availability (e.g., seaweed harvests) or silver market prices can impact costs. Long-term contracts or diversified sourcing may provide price stability.
Indicative Pricing Disclaimer
Prices for silver alginate dressings vary widely based on specifications, order size, and supplier. As of mid-2024, typical FOB prices range from $0.50 to $3.00 per dressing unit, depending on size and silver content. Buyers should request updated quotations tailored to their specific requirements and consider all cost factors outlined above.
By thoroughly understanding the multifaceted cost structure and pricing influences, international B2B buyers can optimize procurement strategies for silver alginate dressings, ensuring high-quality wound care solutions that align with budgetary and regulatory demands across diverse global markets.
Spotlight on Potential silver alginate dressing Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section offers a look at a few manufacturers active in the ‘silver alginate dressing’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct their own extensive due diligence before any engagement. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for silver alginate dressing
Key Technical Properties of Silver Alginate Dressings
1. Material Composition and Grade
Silver alginate dressings are primarily composed of high-purity alginate fibers derived from brown seaweed, combined with medical-grade silver ions. The quality and purity of alginate affect absorbency and biocompatibility, while the silver grade influences antimicrobial efficacy. For B2B buyers, specifying material grade ensures consistent performance, regulatory compliance, and patient safety, especially important for markets with stringent health standards such as Europe.
2. Absorbency Capacity
Absorbency is a critical specification, typically measured by the amount of wound exudate the dressing can hold relative to its weight—often up to 20 times. This property ensures effective management of moderate to heavy exudate wounds, reducing dressing change frequency and lowering overall treatment costs. Buyers should verify absorbency tests and certifications to match product capability with clinical needs.
3. Silver Ion Release Rate
The controlled release of silver ions is essential for sustained antimicrobial action without cytotoxicity. Dressings must balance effective pathogen inhibition with tissue compatibility. B2B purchasers should assess data on ion release kinetics to confirm prolonged protection, especially for chronic wound care markets where infection control is paramount.
4. Gel Formation and Moisture Retention
Upon contact with wound fluid, alginate fibers form a soft gel that maintains a moist wound environment conducive to healing and facilitates autolytic debridement. The gel’s consistency and stability affect patient comfort and ease of dressing removal. Buyers targeting diverse climates, such as humid regions in South America or dry zones in the Middle East, should consider how moisture retention adapts to local conditions.
5. Sterilization Method and Shelf Life
Silver alginate dressings are sterilized using methods such as gamma irradiation or ethylene oxide to ensure product safety without compromising material integrity. The sterilization process impacts shelf life, which typically ranges from 2 to 3 years. International buyers must confirm sterilization certificates and shelf-life guarantees to optimize inventory and avoid wastage.
6. Tolerance and Dimensional Accuracy
Precision in dressing dimensions and thickness is vital for optimal wound coverage and compatibility with secondary dressings. Tolerances in size should be minimal, ensuring consistent fit across batches. This reduces clinical complications and supports supplier reliability, a key factor for bulk purchasing and supply chain stability.
Essential Trade Terminology for Silver Alginate Dressing Procurement
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to companies that produce the dressing products, often supplying them to other brands or distributors. Understanding OEM relationships helps buyers negotiate customization options, pricing, and quality assurance, especially when seeking private-label products for local markets.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest order size a supplier is willing to fulfill. MOQ impacts inventory investment and cash flow. Buyers from emerging markets should negotiate MOQs that align with demand forecasts and storage capacities to avoid overstocking or stockouts.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal process where buyers solicit price and terms from suppliers. RFQs should clearly specify technical requirements such as material grade, absorbency, and packaging standards to receive accurate and comparable bids, facilitating informed procurement decisions.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms defining responsibilities, costs, and risks between buyer and seller during shipping (e.g., FOB, CIF, DDP). Familiarity with Incoterms enables buyers to manage logistics effectively, optimize landed costs, and comply with import regulations across different countries.
CE Marking / ISO Certification
These certifications indicate compliance with international quality and safety standards. CE marking is mandatory for medical devices in the European Economic Area, while ISO 13485 certifies quality management systems for medical products. Buyers should verify these certifications to ensure regulatory acceptance and market access.
Lead Time
The period between placing an order and receiving the goods. Understanding lead time is critical for supply chain planning, especially for markets with variable shipping infrastructure. Buyers should confirm lead times upfront to synchronize procurement with clinical demand and avoid treatment delays.
By thoroughly evaluating these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make well-informed purchasing decisions that optimize wound care outcomes, ensure regulatory compliance, and enhance supply chain efficiency across diverse global markets.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the silver alginate dressing Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global market for silver alginate dressings is expanding rapidly, driven by increasing prevalence of chronic wounds, rising healthcare expenditures, and growing awareness of advanced wound care solutions. For international B2B buyers—especially those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—this sector offers robust opportunities due to the high demand for effective, infection-preventing dressings in both hospital and outpatient settings.
Key market drivers include:
- Rising chronic wound incidence: Conditions such as diabetes and vascular diseases are more prevalent in emerging economies like Brazil and Indonesia, increasing demand for specialized dressings that manage infection and promote healing.
- Technological advancements: Innovations in silver ion release mechanisms and alginate fiber processing enhance dressing efficacy, improving antimicrobial action and absorption rates, which are critical factors for buyers seeking high-performance products.
- Regulatory harmonization: Europe’s stringent medical device regulations are influencing sourcing decisions globally, encouraging suppliers to meet international standards, thus facilitating smoother cross-border trade.
- Cost-efficiency focus: Buyers in emerging markets prioritize dressings that reduce healing time and hospital stays, making silver alginate dressings attractive due to their dual antimicrobial and absorbent properties.
- Supply chain diversification: Geopolitical factors and pandemic-related disruptions have prompted buyers to explore diversified sourcing, including local and regional manufacturers in Africa and the Middle East, to mitigate risks and reduce lead times.
Emerging sourcing trends highlight a shift towards digital procurement platforms and integrated supply chain solutions that provide transparency and traceability. B2B buyers increasingly rely on data-driven supplier evaluations, leveraging certifications and clinical efficacy data to inform purchasing decisions.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a decisive factor in purchasing silver alginate dressings, particularly for buyers in Europe and increasingly in emerging markets where environmental regulations and corporate social responsibility expectations are rising. The production of alginate dressings involves harvesting brown seaweed, and sourcing practices have significant environmental impacts if not managed responsibly.
Key sustainability considerations include:
- Sustainable raw material sourcing: Ethical procurement of alginate involves ensuring seaweed is harvested without damaging marine ecosystems or depleting natural stocks. Buyers should prioritize suppliers certified under recognized marine stewardship programs.
- Reduced chemical footprint: Silver incorporation techniques vary; choosing dressings manufactured with environmentally friendly silver ion release technologies can minimize toxic byproducts and reduce environmental contamination.
- Waste management and biodegradability: Silver alginate dressings, being partly biodegradable due to their natural alginate base, offer advantages over fully synthetic alternatives. However, proper disposal protocols are essential to prevent silver accumulation in the environment.
- Certifications and standards: Buyers should seek products compliant with ISO 13485 (medical device quality management) and environmental certifications such as ISO 14001. Additionally, certifications like Oeko-Tex or equivalents that verify absence of harmful substances can be a differentiator.
- Ethical supply chain transparency: Traceability of both alginate and silver sources is crucial. Buyers benefit from partnering with suppliers who provide full visibility into labor practices, environmental impact, and sustainable harvesting, aligning with growing global demands for corporate responsibility.
Integrating sustainability into sourcing decisions not only supports environmental stewardship but also enhances brand reputation and meets procurement policies in many international healthcare institutions.
Brief Evolution and Historical Context
Silver alginate dressings emerged as a significant advancement in wound care during the late 20th century, combining the absorbent properties of alginate dressings—traditionally used since the 1980s—with the antimicrobial power of silver, which has been recognized since antiquity for infection control. This combination was developed to address limitations of conventional dressings by providing both exudate management and infection prevention in a single product.
Over the past two decades, continuous innovation has improved the controlled release of silver ions and enhanced the biocompatibility of these dressings. This evolution has been driven by clinical demand for faster healing times and reduced infection rates in complex wounds, including diabetic ulcers and surgical wounds. For B2B buyers, understanding this history underscores the maturity and proven efficacy of silver alginate dressings, making them a reliable investment for healthcare providers seeking effective wound management solutions globally.
Related Video: Crude Oil Prices & Global Trade Market Seen Stabilising After Trump Announced Iran Israel Ceasefire
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of silver alginate dressing
-
How can I effectively vet suppliers of silver alginate dressings for international procurement?
To vet suppliers, start by verifying their certifications such as ISO 13485 (medical devices) and CE marking for Europe. Request product samples and third-party lab test reports confirming antimicrobial efficacy and absorbency. Check their track record with references or reviews from other B2B clients, especially those in your region (Africa, South America, Middle East, Europe). Assess their manufacturing capabilities, quality assurance processes, and compliance with regulatory standards applicable in your target markets. Additionally, confirm their ability to provide full documentation like Certificates of Analysis (CoA) and Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS). -
Is it possible to customize silver alginate dressings to meet specific clinical or packaging requirements?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options including dressing size, thickness, silver concentration, and packaging formats to suit different wound care protocols or regional preferences. For example, buyers in tropical climates may prefer moisture-resistant packaging. Discuss your specific clinical needs, regulatory requirements, and branding preferences upfront. Customized products may require minimum order quantities (MOQs) and longer lead times, so clarify these terms early. Working closely with suppliers on customization can enhance product acceptance in local healthcare markets. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for silver alginate dressings in international B2B transactions?
MOQs vary widely depending on the supplier and customization level but typically range from 1,000 to 10,000 units per SKU for standard products. Custom formulations or packaging often necessitate higher MOQs. Lead times generally span 4 to 12 weeks, accounting for manufacturing, quality control, and export logistics. Buyers should confirm these details during contract negotiations and plan inventory accordingly. Establishing a long-term partnership with suppliers can sometimes enable more flexible MOQs and expedited production schedules. -
Which payment terms are standard when sourcing silver alginate dressings internationally, especially from emerging markets?
Common payment terms include a 30% advance deposit with the balance paid before shipment or upon delivery (e.g., via Letter of Credit or Telegraphic Transfer). For new suppliers, upfront payment is often required to mitigate risk. Established buyers may negotiate net 30 or net 60 terms. To reduce financial exposure, consider escrow services or trade finance solutions. Always verify supplier banking details and ensure compliance with international anti-fraud measures. Transparent payment terms and clear contracts are crucial to maintaining trust in cross-border deals. -
What quality assurance certifications should B2B buyers prioritize when importing silver alginate dressings?
Key certifications include ISO 13485 for medical device quality management, CE marking for European conformity, and FDA registration if importing to or through the U.S. market. Suppliers should also provide product-specific documentation such as biocompatibility test results, antimicrobial efficacy studies, and sterility assurances. Compliance with local regulatory authorities in the buyer’s country, such as ANVISA in Brazil or SAHPRA in South Africa, is essential. Prioritize suppliers with robust QA systems that include batch traceability and post-market surveillance capabilities. -
How should international buyers handle logistics and customs clearance for silver alginate dressings?
Coordinate with suppliers to understand packaging dimensions, weight, and HS codes for accurate shipping quotes and customs classification. Choose reliable freight forwarders experienced with medical supplies and your destination countries to ensure smooth customs clearance. Prepare all required documentation: commercial invoice, packing list, certificate of origin, and relevant health certificates. Be aware of import restrictions or additional certifications needed in target markets. Plan for potential delays due to inspections or regulatory reviews, especially in regions with stringent medical import controls. -
What strategies can B2B buyers use to resolve disputes related to silver alginate dressing quality or delivery issues?
Establish clear contract terms detailing product specifications, inspection procedures, delivery schedules, and penalties for non-compliance. Include clauses for third-party quality inspections and dispute resolution mechanisms such as arbitration or mediation. Maintain open communication channels with suppliers to address issues promptly. Document all correspondence and inspection reports. In case of quality disputes, request corrective action plans or replacement shipments. Leveraging trade insurance or escrow arrangements can also protect buyers from financial losses. -
Are there regional considerations for sourcing silver alginate dressings in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe?
Yes, regional factors include regulatory variations, climate, and supply chain infrastructure. For example, humid climates may require moisture-resistant packaging; some countries have specific import licenses or product registrations. Currency fluctuations and trade tariffs can impact pricing and payment terms. Local demand for wound care products may differ, influencing order volumes and product configurations. Engaging local distributors or agents familiar with regional regulations and market dynamics can facilitate smoother market entry and after-sales support.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for silver alginate dressing
Silver alginate dressings represent a critical advancement in wound care, combining superior absorbency with potent antimicrobial protection. For B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the unique benefits—such as effective management of moderate to heavy exudate, infection control, and promotion of faster healing—is essential to making informed procurement decisions. This product’s dual-action mechanism not only improves patient outcomes but also reduces overall treatment costs by minimizing infection risks and dressing change frequency.
Strategic sourcing of silver alginate dressings demands careful supplier evaluation, focusing on product quality certifications, consistent supply chain reliability, and compliance with regional regulatory standards. Buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers or distributors who demonstrate transparency in product composition and have robust logistics capabilities to ensure timely delivery, especially in emerging markets like Indonesia and Brazil.
Looking ahead, the growing global emphasis on advanced wound care solutions, coupled with rising healthcare infrastructure investments in target regions, signals expanding demand for silver alginate dressings. International buyers are encouraged to leverage this momentum by adopting strategic procurement frameworks that balance cost-efficiency with product efficacy. Establishing long-term supplier relationships will be key to navigating market fluctuations and securing competitive advantage in wound care provision.